Maintaining a balanced diet is essential to ensure health and well-being throughout life. One of the most effective guides for structuring a balanced diet is the healthy food pyramid. This article explores the food pyramid in detail, providing valuable information on how to use it to improve your nutrition and quality of life.
What is the Healthy Food Pyramid?
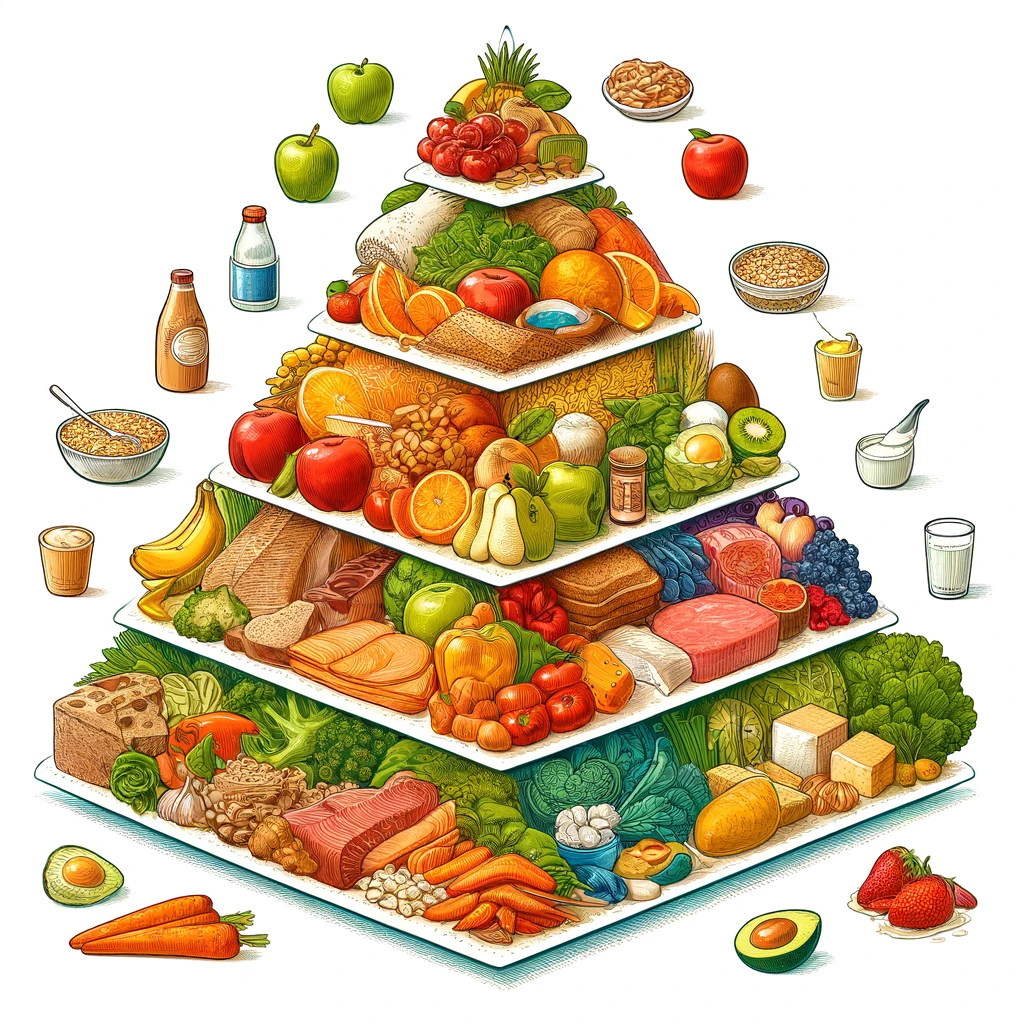
The definition of a food pyramid is a visual representation that illustrates the ideal proportion of different food groups which should be consumed daily. It was developed to help people plan their meals in a balanced way, ensuring that all nutritional needs are met.

History and Evolution of the Food Pyramid
The food pyramid was first introduced in United States by the Department of Agriculture (USDA) in 1992. Since then, it has undergone several revisions to reflect changes in nutritional recommendations and eating habits. The latest version emphasizes the importance of eating whole foods, reducing sugar and saturated fat intake, and increasing fruit and vegetable intake.
Benefits of Following the Food Pyramid
Following a healthy food pyramid can bring numerous health benefits, including:
- Better weight control
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease
- Improved digestion and intestinal function
- Increased energy levels and general well-being
Food Pyramid Structure
Description of the Different Levels of the Pyramid
The food pyramid is made up of different levels, each representing a specific food group. The base of the pyramid includes foods that should be consumed in greater quantities, while the top represents those that should be consumed in moderation.
Food at Each Level of the Pyramid
- Base of the Pyramid: Complex carbohydrates, such as whole-grain breads, rice, pasta and cereals.
- Second level: Fruits and vegetables, which provide essential vitamins, minerals and fiber.
- Third Level: Lean proteins, including meats, fish, eggs, legumes and nuts.
- Fourth Level: Dairy products, such as milk, yogurt and cheese, are important for bone health.
- Top of the Pyramid: Fats and sugars, which should be consumed in moderation.
Recommended Proportions of Each Food Group
To maintain a balanced diet, it is important to follow the proportions recommended by the food pyramid:
- Carbohydrates: 6 to 11 servings daily
- Fruits: 2 to 4 servings daily
- Vegetables: 3 to 5 servings daily
- Proteins: 2 to 3 servings daily
- Dairy: 2 to 3 servings daily
- Fats and sugars: Consume in moderation
Pyramid Food Groups
Carbohydrate Group
Carbohydrates are the body's main source of energy. They are essential for the proper functioning of the brain, muscles and other organs. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, are particularly beneficial because they provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber.
Examples of Foods Rich in Carbohydrates
- Whole grain bread
- Brown rice
- Whole grain pasta
- Oat
- Quinoa
- Sweet potato
Fruit and Vegetable Group
Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are essential for a healthy diet, as they are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants and fiber. They help protect against several diseases, including cancer, heart disease and obesity.
Examples and Variety of Fruits and Vegetables
- Fruits: apple, banana, orange, strawberry, grape, mango
- Vegetables: spinach, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, peppers, pumpkin
Group of Proteins
Importance of Proteins in the Diet
Proteins are crucial for building and repairing body tissues. They are also necessary for the production of enzymes and hormones. Including a variety of protein sources in your diet is important to ensure you get all essential amino acids.
Protein Sources (Animal and Vegetable)
- Animal sources: chicken meat, lean beef, fish, eggs
- Plant sources: beans, lentils, chickpeas, tofu, nuts and seeds
Dairy Group
Role of Dairy in Health
Dairy products are an important source of calcium, vitamin D and protein, essential for bone and dental health. They also contribute to muscle function and blood clotting. Incorporating dairy products into your diet helps maintain strong bones and prevent diseases such as osteoporosis.
Alternatives for Lactose Intolerant
For those who are lactose intolerant or have a milk allergy, there are several alternatives available that are also rich in nutrients:
- Fortified soy milk
- almond milk
- Coconut milk
- Coconut or almond yogurt
- Vegan cheese
Fat Group
Types of Fats (Good and Bad)
Fats are an essential part of the diet, but it is important to choose the right types of fats to consume. Good fats, such as unsaturated fats, help reduce cholesterol and protect against heart disease, while bad fats, such as saturated and trans fats, can increase the risk of health problems.
- Good fats: Unsaturated fats found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds, avocado and oily fish.
- Bad fats: Saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed baked goods, margarine and red meat.
Examples of Healthy Fat Sources
- Olive oil
- Canola oil
- Nuts and seeds
- Avocado
- Oily fish (salmon, sardines)
How to Create a Diet Based on the Food Pyramid
Meal Planning
Planning meals based on the food pyramid involves balancing all food groups throughout the day. A good starting point is to ensure that each main meal includes a portion of carbohydrates, protein, fruit, vegetables and, where possible, dairy.
Tips for Balancing Food Groups
- Variety: Include a wide range of foods from each group to ensure complete nutrient intake.
- Proportion: Follow the portions recommended by the food pyramid to avoid excesses or deficiencies.
- Moderation: Limit your intake of processed foods, sugars and bad fats.
- Hydration: Don't forget to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Examples of Weekly Menus
Menu Example 1
- Breakfast: Natural yogurt with oats and fruits
- Lunch: Grilled chicken breast with brown rice and green salad
- Snack: Baby carrots and hummus
- To have lunch: Vegetable soup with wholemeal toast
Menu Example 2
- Breakfast: Banana smoothie with almond milk and spinach
- Lunch: Quinoa salad with roasted vegetables and chickpeas
- Snack: Apple with peanut butter
- To have lunch: Salmon fillet with sweet potato and steamed broccoli
Healthy Food Pyramid for Different Age Groups
Children and Adolescents
Specific Nutritional Needs
Children and adolescents have unique nutritional needs due to their rapid growth and development. They need an adequate amount of calories, proteins, vitamins and minerals to support these processes.
Adaptations in the Food Pyramid
- Carbohydrates: Prioritize whole grains to provide lasting energy.
- Proteins: Include varied sources such as meat, fish, eggs and legumes.
- Fruits and vegetables: Encourage a wide variety to ensure intake of different nutrients.
- Dairy: Ensure adequate calcium intake for bone development.
- Fats: Focus on healthy fats and limit your consumption of processed foods.
Adults
Health Maintenance and Disease Prevention
For adults, maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for long-term health and the prevention of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease and high blood pressure.
Diet Adjustments for Adults
- Moderation: Control portions to avoid weight gain.
- Variety: Include a wide range of foods from all food groups.
- Fiber: Increase fiber intake to improve digestion.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to maintain adequate hydration.
Elderly
Nutritional Requirements in Old Age
Elderly people need a nutrient-rich diet to maintain health and prevent the loss of muscle and bone mass. Calorie intake may decrease, but nutrient needs remain high.
Importance of Hydration and Supplementation
- Hydration: Increase fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
- Supplementation: Consider calcium, vitamin D and B12 supplements as needed, under medical advice.
- Proteins: Include high-quality proteins for muscle maintenance.
Healthy Food Pyramid and Specific Lifestyles
Vegetarians and Vegans
Adaptations in the Food Pyramid
Vegetarians and vegans can follow the food pyramid with some adaptations to ensure adequate intake of all nutrients.
- Proteins: Include plant-based sources like tofu, tempeh, legumes, nuts and seeds.
- Dairy: Replace with plant-based alternatives fortified with calcium and vitamin D.
- Omega 3: Consume chia seeds, flaxseeds and walnuts to obtain essential fatty acids.
Alternative Sources of Nutrients
- Iron: Consume foods rich in iron such as spinach, lentils and beans, and combine with vitamin C to improve absorption.
- B12 vitamin: Include fortified foods or supplements to avoid deficiencies.
Athletes and Active People
Increased Energy Needs
Athletes and people with an active lifestyle have greater energy and nutritional needs to sustain their physical activity and recovery.
Examples of Diets for Athletes
- Pre workout: Meal rich in complex carbohydrates and lean proteins.
- After training: Combination of proteins and carbohydrates for muscle recovery and energy replenishment.
- Hydration: Drink enough water before, during and after exercise.
Challenges and Myths about a Healthy Food Pyramid
Challenges in Implementing the Food Pyramid
Implementing the healthy eating pyramid can be challenging due to factors such as food availability, personal preferences, and budget constraints. Planning and preparing meals in advance can help overcome these obstacles.
Common Myths and Clarifications
- Myth: All carbohydrates are bad.
- Clarification: Whole carbohydrates are essential for energy and digestive health.
- Myth: Fats should be completely avoided.
- Clarification: Healthy fats are important for brain function and protection against heart disease.
- Myth: Dairy products are essential.
- Clarification: There are nutrient-rich alternatives for those who cannot consume dairy products.
Conclusion
The healthy food pyramid is a valuable tool for guiding food choices and promoting a balanced diet. Following its guidelines can help improve overall health, prevent illness, and maintain long-term well-being. Adopt the food pyramid into your daily routine and enjoy the benefits of balanced nutrition.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the healthy food pyramid?
- The healthy food pyramid is a visual guide that helps you structure a balanced diet, indicating the ideal proportions of each food group.
What are the main food groups in the pyramid?
- Carbs, fruits and vegetables, proteins, dairy, and fats and sugars.
How can I adapt the healthy food pyramid for a vegetarian diet?
- Replace animal proteins with vegetables like tofu, tempeh, legumes, and nuts. Use dairy alternatives fortified with calcium and vitamin D.
Is it possible to follow the healthy food pyramid with budget restrictions?
- Yes, prioritizing whole foods, seasonal fruits and vegetables, and economical protein sources like beans and lentils.
What are the main advantages of following the healthy food pyramid?
- Improves general health, weight control, prevention of chronic diseases, and increased energy levels and well-being.